India’s apprenticeship framework has entered a new era with the notification of the Apprenticeship (Amendment) Rules, 2025, on 11th September 2025. These reforms update the original Apprentices Act of 1961 and are aimed at making apprenticeships more accessible, inclusive, and better aligned with the needs of today’s dynamic workforce. By introducing higher stipends, clearer qualification norms, and stronger inclusion policies, the government is signalling its intent to place apprenticeships at the heart of India’s skilling and employability strategy.
Higher Stipends for Apprentices
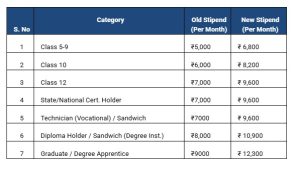
One of the most notable changes in the amendment is the upward revision of stipends for apprentices. For years, low stipends had discouraged both students and workers from pursuing apprenticeship opportunities. The new rules directly address this issue by creating a transparent and progressive structure of minimum monthly stipends across education levels.
Apprentices with education levels of Class 5 to Class 9 will now receive ₹6,800 per month, while those who have completed Class 10 will be entitled to ₹8,200. For apprentices who have completed Class 12, or who hold a State or National Certificate, or are in technician (vocational) and sandwich courses, the stipend has been fixed at ₹9,600. Diploma holders and those in sandwich courses within degree institutions will receive ₹10,900 per month, and graduate or degree apprentices will receive ₹12,300.
By raising these amounts, the amendment ensures that apprenticeships are financially viable and competitive compared to other entry-level opportunities. This change is also expected to encourage more young people to opt for apprenticeship programs, thereby enlarging the skilled talent pipeline available to industry.
Expanding Inclusivity for Persons with Disabilities
Another important element of the amendment is the emphasis on inclusivity. The revised rules align apprenticeship opportunities with the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. Employers are now required to reserve training slots for persons with disabilities, thereby making sure that skilling pathways are accessible to all sections of society.
If the reserved positions remain vacant, the employer is permitted to fill them with other eligible candidates who meet the physical fitness requirements of the program. This provision ensures that inclusivity does not come at the cost of efficiency and that available opportunities are not left unused. The measure reflects a balanced approach, combining affirmative action with practical flexibility for employers.
Formal Recognition of Degree Apprenticeships
The integration of degree apprenticeships into academic programs marks a structural shift in how India approaches skill development. The amendment formally recognises degree apprenticeship as a course embedded within the curriculum of degree and diploma programs. This means that students will no longer have to choose between academic study and workplace learning. Instead, they can gain real-world experience while pursuing their formal education.
This reform has the potential to dramatically improve employability outcomes for graduates. By the time students complete their degrees, they will already have practical experience in their chosen fields. This will make the transition from education to employment smoother, while also providing employers with candidates who are not only academically qualified but also industry-ready.
Guidelines for Multiple Apprenticeship Programs
Until now, there was uncertainty about whether individuals could undertake more than one apprenticeship. The amended rules provide clarity by allowing a person to take up to two apprenticeships during their career. However, there are specific conditions attached. The second apprenticeship must be in a different trade than the first, and it will not carry a government stipend.
This provision strikes a balance between flexibility for learners and safeguards against misuse of the scheme. It allows individuals to diversify their skillsets and explore multiple industries, while ensuring that stipends remain targeted toward first-time apprentices who need them most.
Expanded Eligibility Criteria
The amendment also simplifies and clarifies who is eligible to become an apprentice. Eligibility is now tied directly to the educational qualifications listed in Schedule IA of the Act. This provides students, job seekers, and employers with a clear framework to determine who qualifies for apprenticeship training.
For example, degree apprentices will require approval after the completion of their final examinations unless they are specifically cleared by Apprenticeship Advisers. These provisions bring much-needed clarity to the system, reducing confusion for both participants and employers.
What the Apprenticeship Amendments Mean for Employers?
For employers across industries, these changes bring both opportunities and responsibilities. On one hand, stipend budgets, contracts, and onboarding processes will need to be updated to comply with the revised rules. On the other hand, organisations now have access to a wider and more diverse pool of apprentices.
By reserving places for persons with disabilities, integrating apprenticeships with academic programs, and offering higher stipends, the reforms make apprenticeships more attractive to young people. Employers stand to benefit from a steady pipeline of motivated, better-prepared candidates who can be groomed for long-term roles.
Building a Future-Ready Workforce
The amendments to the Apprentices Act are more than just a policy update. They are a recognition of the crucial role apprenticeships can play in preparing India’s workforce to navigate the challenges of the future. By raising stipends, broadening access, and integrating apprenticeships into education, the government has strengthened the apprenticeship system as a key pillar of skill development.
For students, these changes make apprenticeships a more appealing and financially rewarding choice. For employers they offer a structured pathway to cultivate talent. Taken together, the reforms represent a significant step toward building a workforce that is not only larger but also more skilled, inclusive, and future-ready.